|
The general QAM transmitter and receiver block diagram:
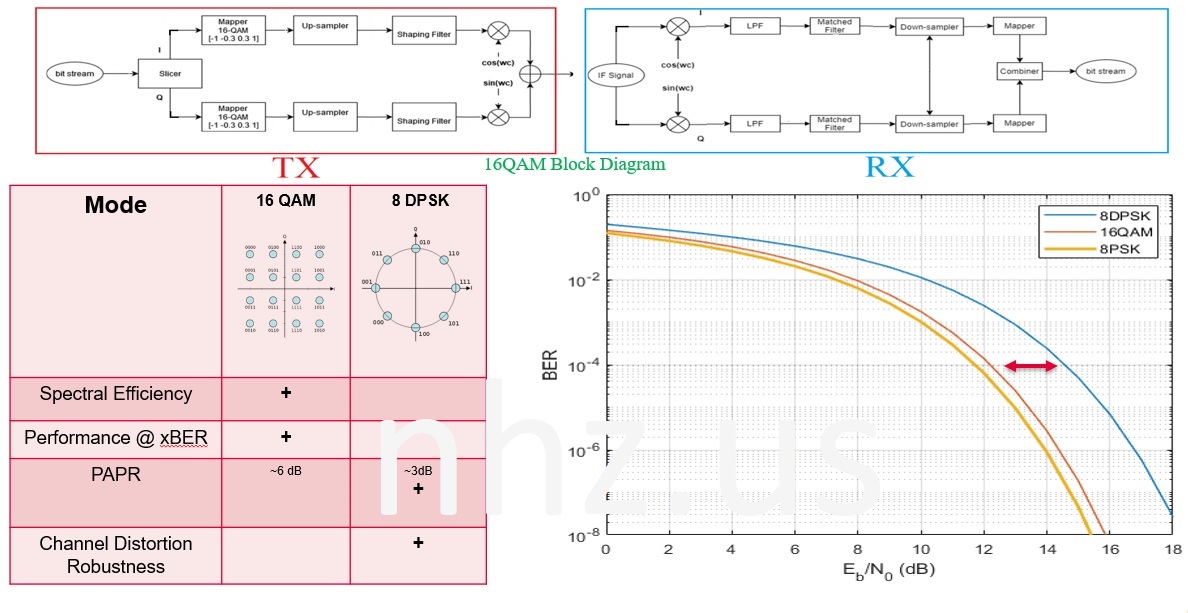
comparison of 16QAM and 8DPSK
16 QAM
and 8DPSK (8PSK) are two different modulation schemes used in digital
communication systems. Here are some key differences between the two:
- Constellation
Diagrams: 16 QAM uses a constellation diagram with 16 points, while 8DPSK
uses a constellation diagram with 8 points. This means that 16 QAM is
capable of transmitting 4 bits of information per symbol, while 8DPSK is
capable of transmitting 3 bits of information per symbol.
- Spectral
Efficiency: Due to its higher number of points on the constellation
diagram, 16 QAM is more spectral efficient than 8DPSK. This means that 16
QAM can transmit more information per unit of bandwidth compared to 8DPSK.
- Robustness:
8DPSK is generally more robust than 16 QAM in noisy environments because
it uses fewer points on the constellation diagram. This means that it is
less susceptible to errors caused by noise and interference.
- Implementation
Complexity: 16 QAM is more complex to implement than 8DPSK due to its
higher number of points on the constellation diagram. This means that 16
QAM requires more processing power and more complex hardware than 8DPSK.
- Applications:
16 QAM is commonly used in high-speed data transmission applications such
as cable modems, digital subscriber line (DSL) modems, and wireless local
area networks (WLANs). 8DPSK, on the other hand, is commonly used in
satellite communications, mobile phones, and digital audio broadcasting.
In summary, while both
16 QAM and 8DPSK are commonly used in digital communication systems, they
differ in terms of their constellation diagrams, spectral efficiency,
robustness, implementation complexity, and applications. The choice of which
modulation scheme to use depends on the specific requirements of the
application.
|
