Understanding Harmonic Distortion as Part of RF Analog Nonlinearity EffectIn RF (Radio Frequency) systems, harmonic distortion is a significant consequence of nonlinear behavior in RF components. It refers to the generation of unwanted harmonic frequencies that are integer multiples of the original signal frequencies. Understanding harmonic distortion is crucial for designing RF systems that maintain signal purity and minimize interference. What is Harmonic Distortion?Harmonic distortion occurs when an RF device produces harmonics—additional frequencies that are integer multiples (2nd, 3rd, etc.) of the original signal frequency. These harmonics are unwanted and can interfere with nearby communication channels and degrade system performance. Causes of Harmonic DistortionHarmonic distortion in RF systems primarily arises due to the nonlinear response of components such as amplifiers, mixers, and oscillators. When driven by high-amplitude signals, these components produce nonlinearities that result in harmonic frequencies. Types of Harmonic DistortionThere are several types of harmonic distortion:
Impact of Harmonic DistortionHarmonic distortion can impact RF systems in several ways:
Measurement and MitigationEngineers use various methods to measure and mitigate harmonic distortion in RF systems:
ExamplesExample 1: Second Harmonic Distortion in an RF AmplifierWhen testing an RF amplifier, engineers observe the presence of second harmonic distortion at twice the input signal frequency. This distortion can be minimized by using linear amplifiers and applying filtering techniques. Example 2: Mitigating Third Harmonic Distortion in a TransmitterIn a transmitter system, third harmonic distortion can interfere with nearby communication channels. Engineers mitigate this by designing filters that attenuate third harmonics and optimizing transmitter design for minimal distortion. ConclusionHarmonic distortion is a significant aspect of RF analog nonlinearity, affecting signal purity and system performance. By understanding its causes, types, and mitigation techniques, engineers can design RF systems that minimize distortion, enhance signal quality, and optimize overall performance in various applications. Question & AnswerQ: What is harmonic distortion in RF systems? A: Harmonic distortion refers to the generation of unwanted harmonic frequencies that are integer multiples of the original signal frequency due to nonlinearities in RF components. Q: How does harmonic distortion affect RF systems? A: Harmonic distortion can lead to interference with adjacent channels, reduced signal purity, and decreased system efficiency in RF communication and transmission systems. Q: How can harmonic distortion be mitigated? A: Harmonic distortion can be mitigated by designing linear RF components, implementing filtering techniques, and optimizing system design to minimize nonlinear effects and harmonic generation. 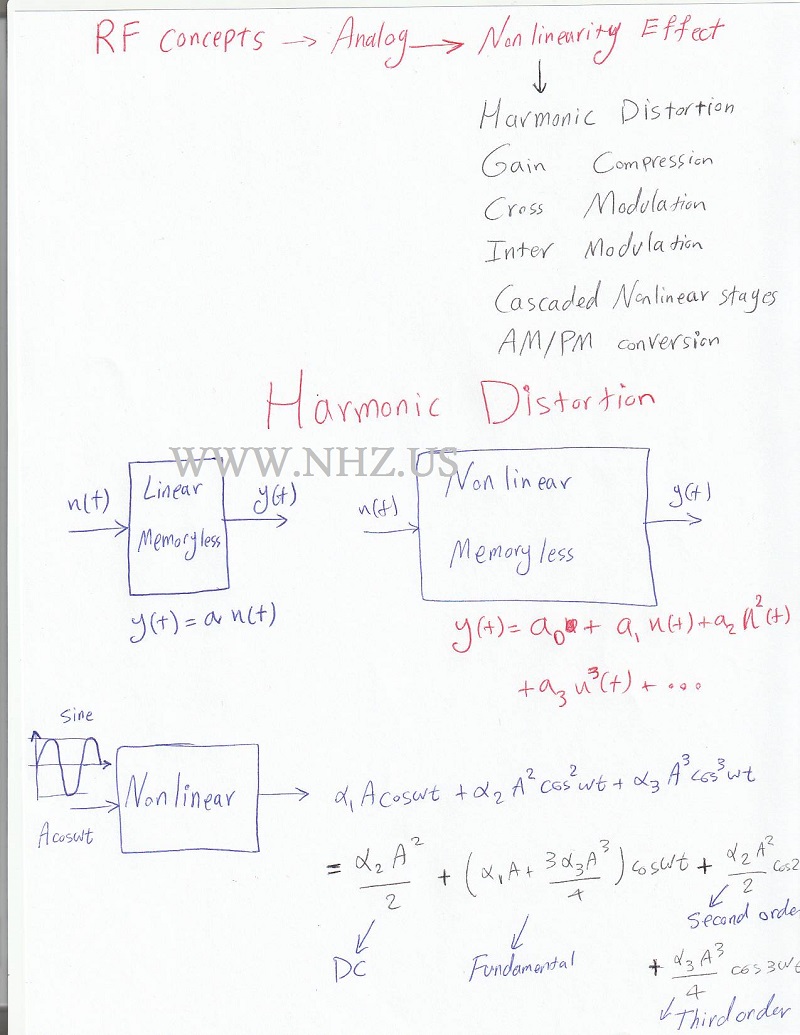   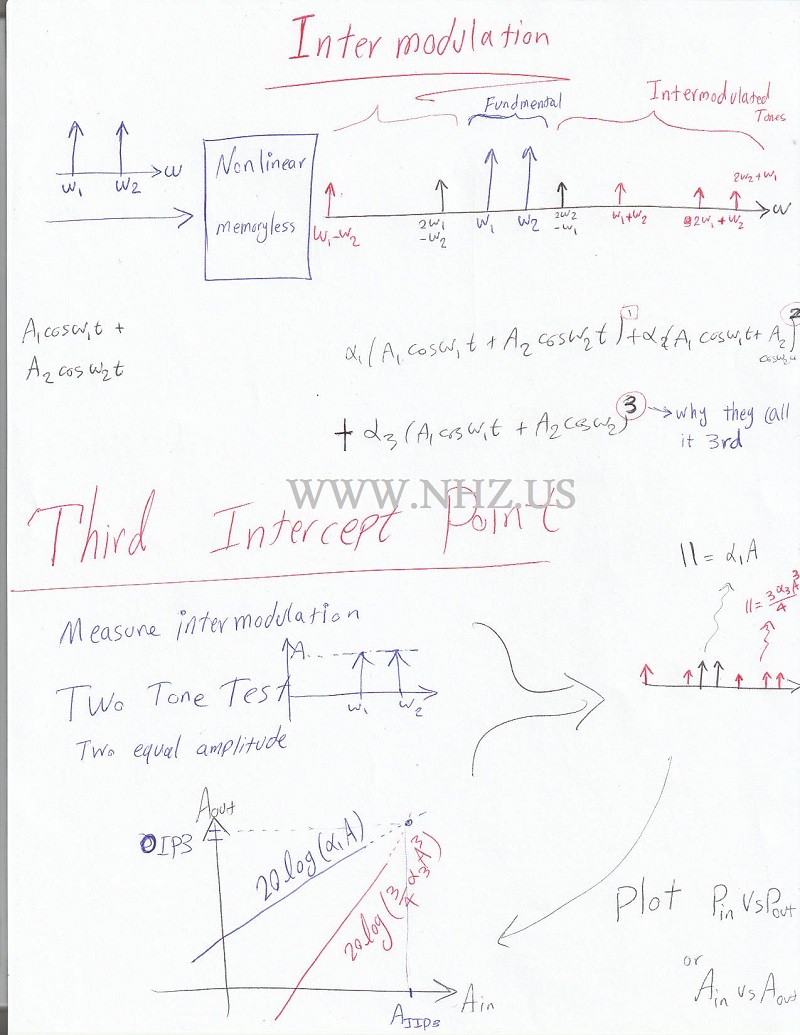 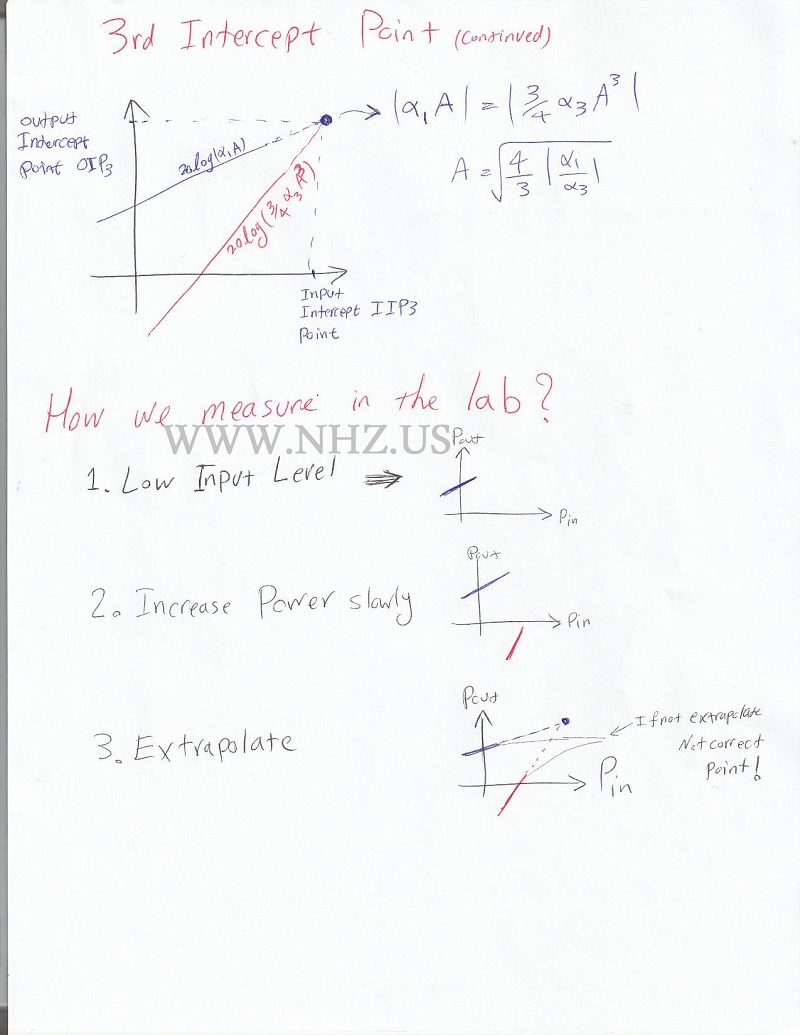 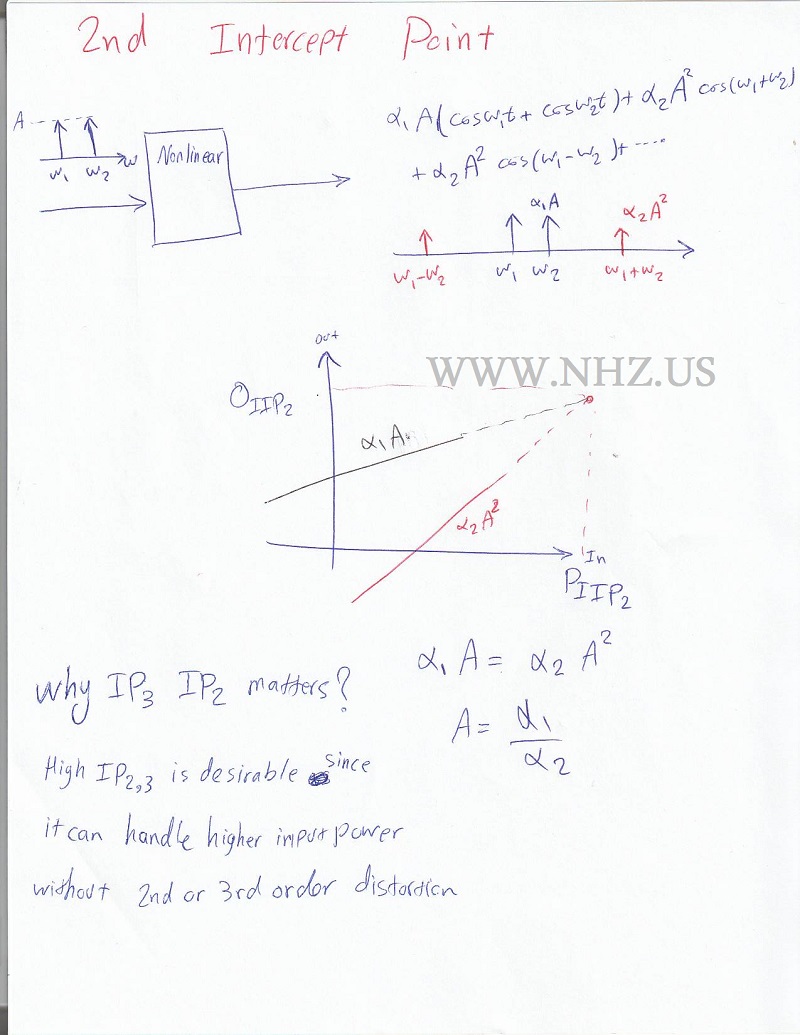 |